Source: IoTnow

According to a recent report, 71% of Internet of Things (IoT) adopters in the public sector reported cost savings, and 70% said IoT solutions had improved their visibility into organsational operations. From sanitation to safety, says Jeremy Prince, president of Sigfox USA, IoT applications allow for better insight into how and where municipal resources should be used meaning cities only stand to benefit from IoT adoption.
Yet, two main obstacles stand in the way of municipal / public sector adoption of IoT solutions; the cost and the security of networks and devices. In fact, 57% of respondents in a recent survey stated security concerns as the number one barrier to greater IoT adoption, followed by a lack of budget (27%).
To overcome these barriers, municipalities considering IoT adoption may consider new networks and technologies that require lower upfront investment and recurring costs than traditional options and ensure top-notch security. One such available option is the 0G network.
What is a 0G Network?
A 0G network is a dedicated, low-bandwidth wireless network specifically designed to connect simple, low-powered and low-cost IoT devices to the internet. The simplicity of 0G means that cities can avoid IoT solutions that require SIM cards, which can cost up to US$40 (£31) per device. Rather, by connecting IoT devices to a 0G network that allows the transmission of small amounts of data over long ranges, smart city stakeholders can get the IoT-enabled insights they need to steer decisions at a significantly lower cost than traditional network options. And because 0G is low energy, the devices experience longer battery life and less maintenance to keep devices running smoothly, while keeping costs low.
0G networks are more secure than other traditional networks.
0G does not enable traditional two-way communication sessions; instead, once the IoT device sends the data to the base station, it goes into sleep-mode. This creates an extremely small window during which hackers can break into the network and take control of the device. As such, devices communicating over a 0G network are not “always connected” and, therefore, significantly less susceptible to network attacks.
0G Key Principles
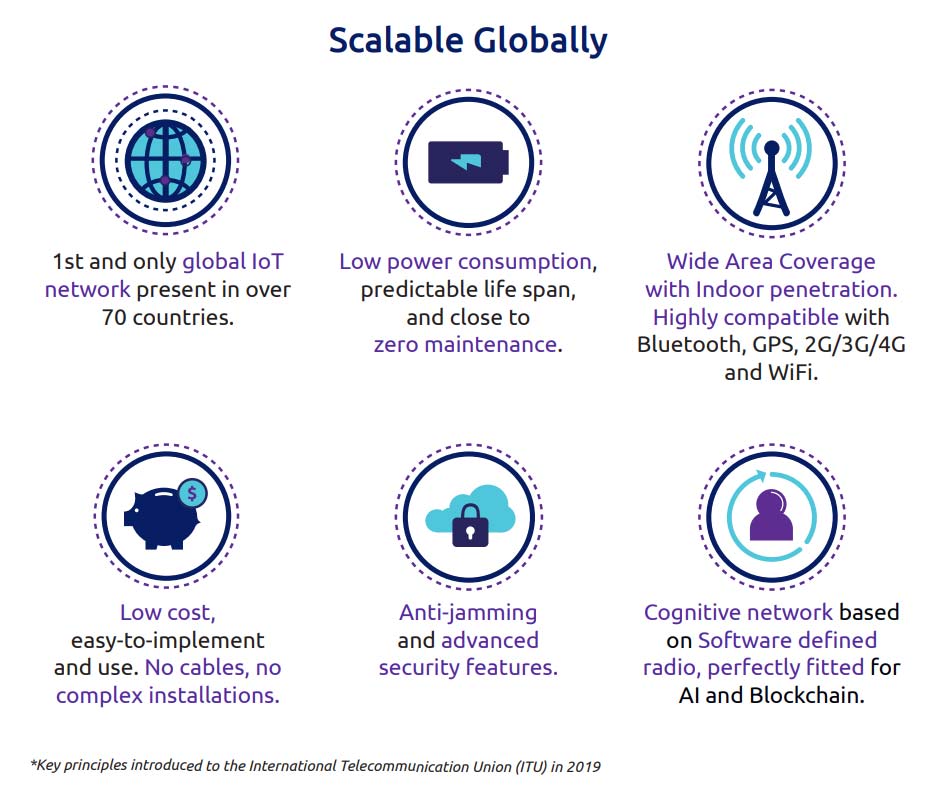
How are Smart Cities Using 0G Today?
By connecting IoT devices to a 0G network, smart cities can overcome cost and security barriers and harness the power of the IoT. Already, some smart cities are using data collected from IoT devices that are connected to a 0G network to secure valuable insights that will ultimately improve the lives of their citizens.
For example, in Spain, IoT devices connected to a 0G network are attached to streetlights. This application helps local governments better understand and optimise their energy consumption by automating predictive maintenance and improving lighting quality. In England, 0G-connected IoT solutions are being used to alert home and building owners of leaks, tempering the impact of water damage. And in Denmark, IoT solutions connected to a 0G network signal when trash bins are full so that garbage can be collected more efficiently resulting in cleaner, healthier urban environments.
These are just some of the ways IoT solutions can create smart cities. Public safety officials can also use IoT devices to detect gunshots, ensure fire hydrants are in proper working condition and determine the structural integrity of city infrastructure.
The power of the IoT can only be fully experienced when devices are deployed on a large scale and running efficiently. By turning to 0G, city officials can enable cost-efficient, secure IoT applications that will drive innovation in smart cities for years to come.
The author is Jeremy Prince, president of Sigfox USA.
About WNDUK
WND UK, is the UK #0G secure sensor data network operator, powered by Sigfox. The public network, which was deployed in a period of just 18 months, covers over 90% of the UK’s population. WND is now continuing to strengthen our network through densification and by working with channel partners to achieve deep in-building coverage where required.
Sigfox is the world’s first global dedicated low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) communications service for sensor data, typically deployed in Internet of Things (IoT) applications. WND UK’s network solution provides reliable and affordable communications for sensor devices that require very little power.
WND UK’s growing ecosystem of channel partners operate across a broad range of industry sectors providing a range of applications, such as the monitoring of legionella in healthcare and public sector buildings, automated meter readings for utilities, property technology, leak detection and asset management within logistical, returnable packaging and post and parcel sectors. Learn more: WND Technology Overview



